Leetcode•Sep 16, 2025
Guess Number Higher or Lower II
Hazrat Ali
Leetcode
We are playing the Guessing Game. The game will work as follows:
- I pick a number between
1andn. - You guess a number.
- If you guess the right number, you win the game.
- If you guess the wrong number, then I will tell you whether the number I picked is higher or lower, and you will continue guessing.
- Every time you guess a wrong number
x, you will payxdollars. If you run out of money, you lose the game.
Given a particular n, return the minimum amount of money you need to guarantee a win regardless of what number I pick.
Example 1:
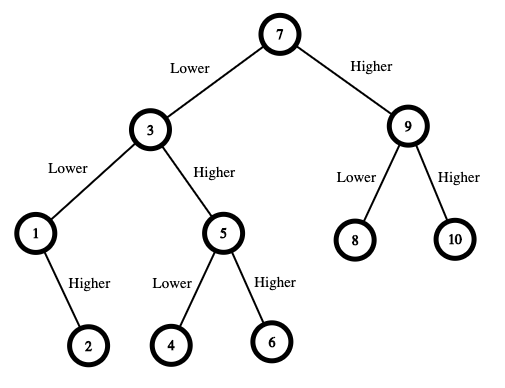
Input: n = 10 Output: 16 Explanation: The winning strategy is as follows: - The range is [1,10]. Guess 7. - If this is my number, your total is $0. Otherwise, you pay $7. - If my number is higher, the range is [8,10]. Guess 9. - If this is my number, your total is $7. Otherwise, you pay $9. - If my number is higher, it must be 10. Guess 10. Your total is $7 + $9 = $16. - If my number is lower, it must be 8. Guess 8. Your total is $7 + $9 = $16. - If my number is lower, the range is [1,6]. Guess 3. - If this is my number, your total is $7. Otherwise, you pay $3. - If my number is higher, the range is [4,6]. Guess 5. - If this is my number, your total is $7 + $3 = $10. Otherwise, you pay $5. - If my number is higher, it must be 6. Guess 6. Your total is $7 + $3 + $5 = $15. - If my number is lower, it must be 4. Guess 4. Your total is $7 + $3 + $5 = $15. - If my number is lower, the range is [1,2]. Guess 1. - If this is my number, your total is $7 + $3 = $10. Otherwise, you pay $1. - If my number is higher, it must be 2. Guess 2. Your total is $7 + $3 + $1 = $11. The worst case in all these scenarios is that you pay $16. Hence, you only need $16 to guarantee a win.
Example 2:
Input: n = 1 Output: 0 Explanation: There is only one possible number, so you can guess 1 and not have to pay anything.
Example 3:
Input: n = 2 Output: 1 Explanation: There are two possible numbers, 1 and 2. - Guess 1. - If this is my number, your total is $0. Otherwise, you pay $1. - If my number is higher, it must be 2. Guess 2. Your total is $1. The worst case is that you pay $1.
Solution
/**
*
* @param {number} n
* @return {number}
*/
const getMoneyAmount = n => {
const dp = Array(n + 2)
.fill()
.map(() => Array(n + 2).fill(0));
for (let len = 2; len <= n; len++) {
for (let start = 1; start + len - 1 <= n; start++) {
const end = start + len - 1;
dp[start][end] = Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER;
for (let i = start; i <= end; i++) {
const val = i + Math.max(dp[start][i - 1], dp[i + 1][end]);
dp[start][end] = Math.min(dp[start][end], val);
}
}
}
return dp[1][n];
};